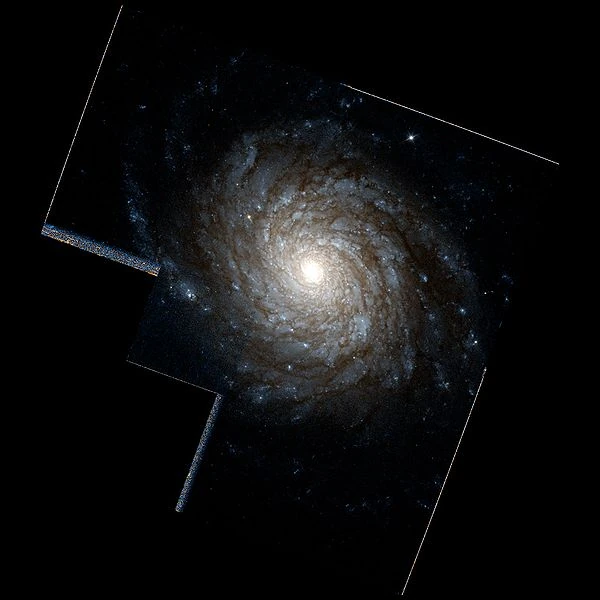
NGC 4030 is a grand design spiral galaxy located about 64 million light years away in the constellation Virgo. It is a member of the NGC 4030 Group of galaxies, which is a member of the Virgo II Groups, a series of galaxies and galaxy clusters strung out from the southern edge of the Virgo Supercluster. With an apparent visual magnitude of 10.6, it is visible with a small telescope as a 3 arc minute wide feature about 4.75° to the southeast of the star Beta Virginis. It is inclined by an angle of 47.1° to the line of sight from the Earth and is receding at a velocity of 1,465 km/s.
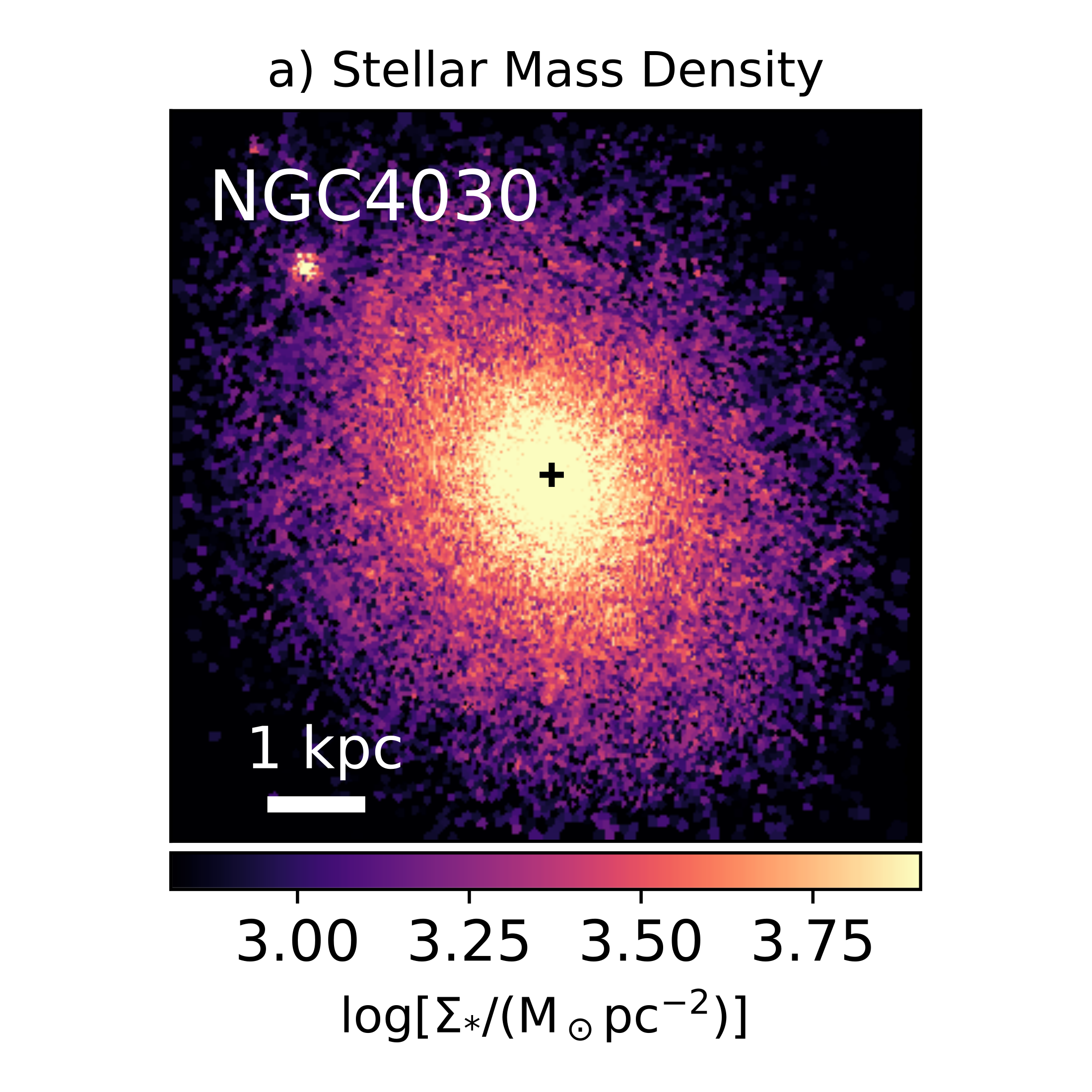
The morphological classification of NGC 4030 in the De Vaucouleurs system is SA(s)bc, which indicates a spiral structure (SA) with no bar (s) and moderate to loosely wound arms (bc). The inner part of the galaxy shows a complex structure with multiple spiral arms, which becomes a symmetric, double arm pattern beyond 49″ from the core. The central bulge is relatively young with an estimated age of two billion years, while the nucleus is inactive.
In 2007, a supernova explosion was discovered in the galaxy from images taken on February 19 from the 1 m Swope telescope at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. Designated SN 2007aa, it was a type IIP supernova positioned 68″.5 north and 60″.8 east of the galactic nucleus. The progenitor was a red giant star with 8.5–16.5 times the mass of the Sun.
Gallery
References
External links
- Media related to NGC 4030 at Wikimedia Commons